Explain the Two Different Categories of Application Layer Protocols
TFTP stands for. Contention-based protocols with reservation mechanisms Synchronous protocols.
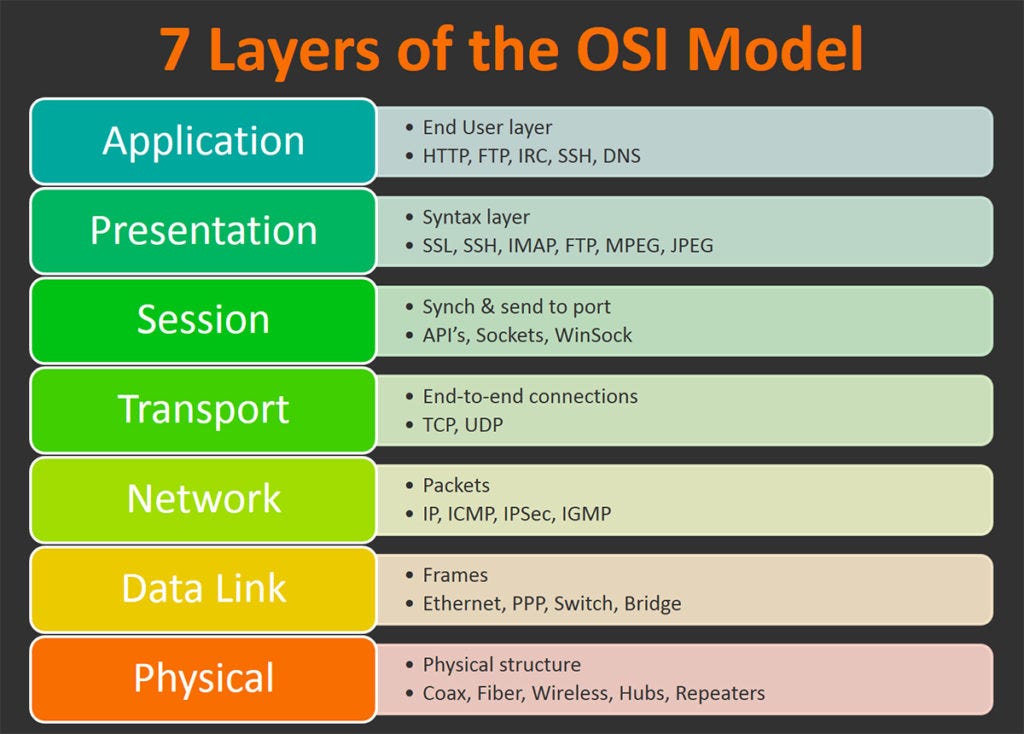
Day 51 Understanding The Osi Model By Anonymous Medium
Types of Application Layer Protocols.

. The User Datagram Protocol UDP does not guarantee delivery thus UDP is called a connectionless protocol. TCP is used by applications such as Web browsers and email. Most applications such as web browsers or e-mail clients incorporate functionality of the.
The UDP protocol enables DDSI and there are DDSI implementations on. All node are kept synchronized. Application presentation and session.
Post Office Protocol 3 POP3 and Internet Message Access Protocol 4 IMAP4 are two application-layer protocols used for electronic messaging across the Internet. FTP File Transfer Protocol. Originally the OSI model consisted of two kinds of application layer services with their related protocols.
Application programs that provide services to a user such as a browser and Web server using the HTTP Application layer protocol. Each of the protocol has its own role and importance. Application layer protocols founded on TCP and UDP solve the communication challenges faced in an IoT project.
This service includes guaranteed delivery of application-layer messages to the destination and flow control that is senderreceiver speed matching. Relative time information is used to achieve effecting reservations. We will study these protocols into two parts.
Protocols which help and support protocols used by usersFor example DNS. Explain the two different categories of Application layer protocols and then detail the PDU used at this layer. Application layer protocols can be broadly divided into two categories.
Application layer protocols are used by programs that fall into two categories. The functionality of the TCPIP application layer protocols fits roughly into the framework of the top three layers of the OSI model. ARP Address Resolution Protocol ARP maps dynamic IP Layer 3 with MAC addresses Layer 2.
Protocols which are used by usersFor email for example eMail. It also provides addressing services at the network layer. The two different categories of Application layer protocols are HTTP and SNMP.
The HTIP protocol transfer data in the form of plain text hyper text audio video and so on. There are several protocols which work for users in Application Layer. Contention-based protocols with scheduling mechanisms.
The file transfer protocol is abbreviated as FTP. For example MACAPR RTMAC. FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol.
A few of the majorly deployed protocols which we will discuss here include DNS FTP HTTP MIME SMTP LDP and DHCP. Explain the two different categories of Application layer protocols and then detail the PDU used at this layer. The Transmission Control Protocol TCP makes a connection with the end host checks whether the data is received and resends it if it is not.
Some of the popular IOT application layer protocols are as follow MQTT SMQTT CoAP DDS XMPP AMQP RESTful HTTP MQTT-SN STOMP SMCP LLAP SSI LWM2M M3DA XMPP-IOT ONS 20 SOAP Websocket Reactive Streams HTTP2 JavaScript IOT MQTT Message Queuing Telemetry Transport is a lightweight messaging protocol. It is a application layer protocol that is used for transforming a file. These two sublayers are the common application service element CASE and specific application service element SASE.
DNS Domain Name System - a distributed database system that works at the transport layer to provide name-to. TCP provides a connection-oriented service to its applications. This tutorial is the Part-1 and here we will discuss DNS FTP SMTP and MIME protocols.
For example D-PRMA CATA HRMA SRMAPA FPRP. FDB stores MAC addresses of the discovered devices and their respective ports. In the Internet there are two transport protocols TCP and UDP either of which can transport application-layer messages.
HTTP provides services to a user such as a browser while SNMP provides services to the system to monitor and gather information about the network traffic and it alerts network admins about conditions that. It is beneficial to terminal. Utility programs that provide services to the system such as SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol programs that monitor and.
Protocols of Application layer 1. Telnet is an application protocol. It provides bidirectional interactive text orientated communication.
Multi-link trunking Protocol MLT. ARP translates 32-bit addresses to 48-bit and vice versa and is preferred by IPv4 devices. The telecommunications network is referred to as Telnet.
A POP3 server receives an e-mail message and holds it for the user. TCP Transmission Control Protocol - the Internet protocols main transport layer protocol. POP3 is a protocol that involves both a server and a client.
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol HTTP the Webs main application-layer protocol although current browsers can access other types of servers A respository of information spread all over the world and linked together. This protocol is preferred for discovering switches. Few of Application layer protocols are described below.
The TCP protocol enables the XMPP MQTT and RESTHTTP communication protocols. ARP Address Resolution Protocol DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol IMAP4 Internet Message Access Protocol SIP Session Initiation Protocol RTP Real-Time Transport Protocol RLP Resource Location Protocol RAP Route Access Protocol L2TP Layer Two Tunnelling Protocol PPTP.

The Internet Protocol Suite Article Khan Academy
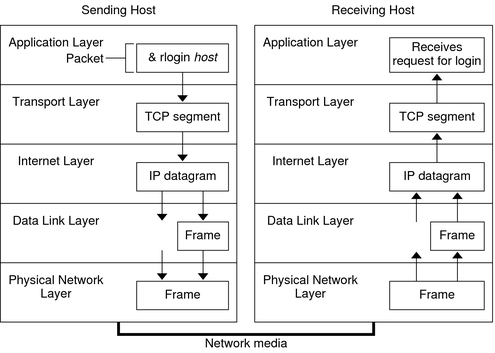
How The Tcp Ip Protocols Handle Data Communications System Administration Guide Ip Services
No comments for "Explain the Two Different Categories of Application Layer Protocols"
Post a Comment